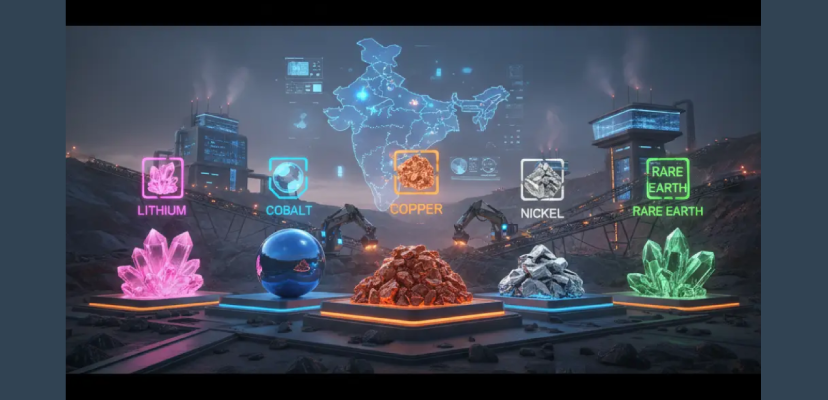
Critical minerals have emerged as the new foundation of global economic strength, central to clean energy technologies, digital infrastructure, and advanced manufacturing. As the world accelerates toward a low-carbon future, the demand for minerals such as lithium, cobalt, rare earth elements, graphite, and copper is rising at an unprecedented pace. In this shifting geopolitical and industrial landscape, Gujarat Mineral Development Corporation (GMDC) is positioning itself as a national leader in developing India’s critical mineral ecosystem.
The Global Critical Minerals Imperative
The International Energy Agency estimates that the market for energy-transition minerals will more than double to USD 770 billion by 2040. Between 2024 and 2050, nearly 3 billion tonnes of minerals will be required to support global clean-energy technologies, and this figure rises to 6 billion tonnes for a net-zero pathway.
India, despite its growing manufacturing capabilities and ambitious clean-energy targets, remains heavily dependent on imports for minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Over 80% of lithium and 42% of natural graphite are currently imported from China, highlighting the urgent need for domestic capability building
India’s Strategic Response: The National Critical Mineral Mission
Recognizing the need for self-reliance, the Government of India launched the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) between FY 2024–25 and FY 2030–31. Backed by ₹16,300 crore in government funding and an expected ₹18,000 crore investment from public sector enterprises, the mission aims to:
This mission is not just economic; it is strategic, ensuring India’s long-term supply security for green technologies, electronics, defence applications, and advanced manufacturing.
GMDC: Transforming Into a Critical Minerals Powerhouse
GMDC is undergoing a major strategic transformation, from a traditional mining enterprise to a future-ready, technology-driven, diversified mineral solutions provider. Its expansion into rare earth elements (REE), copper, fluorspar, and other high-value minerals reflects an ambition aligned with India’s national priorities.
GMDC is building capabilities not only in mining but also in beneficiation, processing, forward integration, and global partnerships, positioning itself to become a key contributor to the NCMM vision.
Lakshya 2030: GMDC’s Roadmap for Sustainable Growth
Unveiled at the Manthan event in Bhubaneswar, GMDC’s Lakshya 2030 outlines a ₹15,000-crore strategic roadmap built on five pillars:
Ambadungar Rare Earth Project: Building India’s REE Supply Chain
Among GMDC’s most transformative projects is the Ambadungar Rare Earth Elements (REE) Project in Chhota Udepur, Gujarat. Geological data handed over by the Atomic Minerals Directorate confirms that Ambadungar is one of the largest known rare earth deposits in the world.
GMDC has committed ₹5,000 crore to develop this asset, aiming to produce 12,000 tonnes of rare earth oxides (REO) annually by FY 2028. The project spans the entire REE value chain, from mining and beneficiation to separation and production of high-value oxides like Nd, Pr, La, and Ce.
This will significantly reduce India’s reliance on imports for critical components used in EV motors, wind turbines, electronics, and defence technologies.
The Ambaji Copper Project: Strengthening India’s Industrial Backbone
GMDC’s Ambaji Copper Project marks Gujarat’s first underground multi-metal mine. Spread across 185 hectares, the deposit holds an estimated 10 million tonnes of copper, zinc, and lead, valued at ₹22,000 crore.
Copper is crucial to renewable energy systems, EVs, grid expansion, and modern infrastructure. With India currently importing 90% of its copper, this project will play a pivotal role in strengthening supply security. Domestic production increased 12.5% in FY 2024–25, driven primarily by mobility and infrastructure demand, indicating strong long-term market potential.

10 million tonnes of copper
A Wider Critical Mineral Portfolio
Beyond rare earths and copper, GMDC is expanding into:
GMDC’s ₹4,500-crore investment across critical minerals strengthens India’s position in sectors such as:
Its forward-integration strategy, especially for silica sand processing, aims to bolster India’s solar manufacturing value chain.
Driving Innovation: GMRICS and Technology Leadership
GMDC has revitalized the GMDC Research and Innovation Centre for Sustainable Development (GMRICS) to lead mineral exploration, extraction, and processing R&D. Strategic MoUs with premier academic and industry institutions are enabling advancements in:
GMDC’s sustainability commitment includes transitioning to electric/hybrid mining fleets and energy-efficient systems, aligning with global ESG benchmarks.
The Role of iCEM: Building a Future-Ready Ecosystem
The International Centre of Excellence in Mining Safety & Automation (iCEM) acts as the technological backbone for India’s critical mineral ambitions. By promoting automation, precision mining, real-time monitoring, and environmental compliance, iCEM strengthens GMDC’s ability to develop critical minerals responsibly and efficiently.
GMDC at the Forefront of India’s Critical Mineral Revolution
As India prepares for a future defined by clean energy, digital acceleration, and industrial growth, critical minerals will shape its economic trajectory. GMDC, through its strategic foresight, robust investments, technological innovation, and alignment with national priorities, is emerging as a cornerstone of India’s mineral self-reliance.
By building world-class capabilities across exploration, processing, and value-chain integration, GMDC is not only securing India’s mineral future but also contributing to a resilient and sustainable global supply landscape.
19 Nov, 2025